 What’s New?
What’s New?
- Cause of well casing pipe damage and repairing technology
- How many steps are needed in the process of pipelines built?
- What are the commonly used welding methods for oil pipelines
- Do you know new anti-corrosion technologies for pipelines
- Development trend of global continuous pipe drilling technology
Technological process for OCTG casing and tubing
Productive process of OCTG casing and tubing
Technological Process
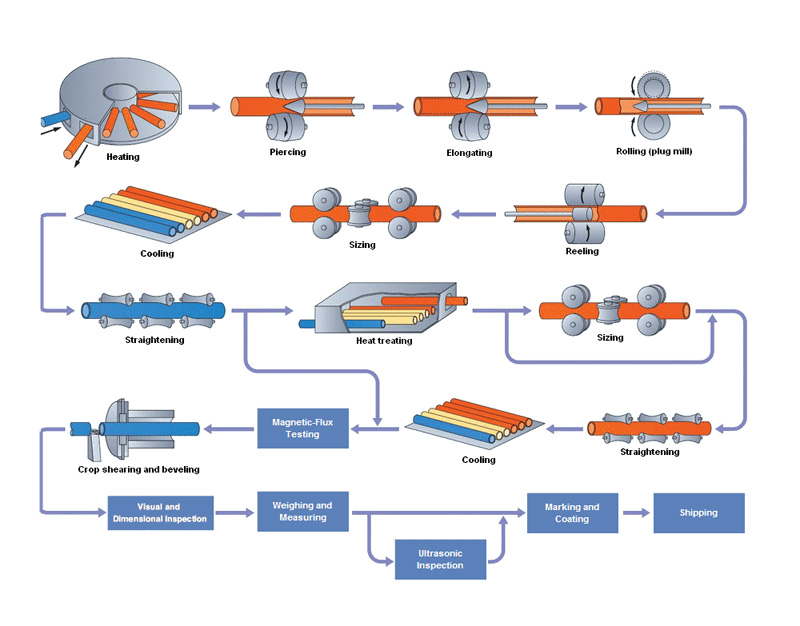
Ingot heating→Perforation→Rolling and sizing→Cooling→Straightening→NDT→End cutting→Coupling thread→Hydraulic test→Painting and thread protecting→Packing
Ingot heating
 Ingot heating is a working procedure which make ingot meet the required temperature of the hot working process. The purpose of the ingot heating is to make the steel ingot have enough plasticity, reduce rolling deformation resistance, improve the internal organization.
Ingot heating is a working procedure which make ingot meet the required temperature of the hot working process. The purpose of the ingot heating is to make the steel ingot have enough plasticity, reduce rolling deformation resistance, improve the internal organization.
Heating process of ingots mainly has two stages: heating stage (including low temperature and high temperature), the ingot surface temperature is increased to the tapping temperature; Uniform heating, to make ingot inside and outside temperature uniformity.
Rolling and sizing
 Hot rolling can reduce energy consumption and cost significantly. The high metal plastic deformation and low deformation resistance, greatly reduce the energy consumption of hot rolled steel.
Hot rolling can reduce energy consumption and cost significantly. The high metal plastic deformation and low deformation resistance, greatly reduce the energy consumption of hot rolled steel.
Hot rolling can improve the process performance of metal, eliminate casting defects and improve the processing performance of the alloy.
Hot rolled usually adopt large ingot casting, which not only improve the production efficiency, but also improve the rolling speed, to achieve continuous rolling process and create the conditions for automation.
Cooling
 After the cooling, hot rolled steel tube is in a specific range. Compared to the traditional process of making the process, it can simplify the process, save energy, get the same or better mechanical properties.
After the cooling, hot rolled steel tube is in a specific range. Compared to the traditional process of making the process, it can simplify the process, save energy, get the same or better mechanical properties.
NDT
 Nondestructive Testing, shorted for NDT, is a widely-used method in pipeline inspection. It is a process of testing, inspecting and evaluating the quality and characteristics of the material without damaging the pipeline itself or affecting the later regular work of the pipe. In other words, after NDT testing, the part can still be put into practical use. NDT utilizes the changes in heat, sound and magnets caused by abnormal inner structure or flaws to inspect the internal and external defects of the material.
Nondestructive Testing, shorted for NDT, is a widely-used method in pipeline inspection. It is a process of testing, inspecting and evaluating the quality and characteristics of the material without damaging the pipeline itself or affecting the later regular work of the pipe. In other words, after NDT testing, the part can still be put into practical use. NDT utilizes the changes in heat, sound and magnets caused by abnormal inner structure or flaws to inspect the internal and external defects of the material.
The common inspection methods of NDT are visual testing (VT), ultrasonic testing (UT), radiographic testing (RT), hydrostatic testing.
Coupling thread
 Threaded joints refers to the pipeline connecting piece with the screw thread, is a most common pipe in industry. Coupling thread makes connection of the pipe becomes more simple, replacement are also more easily and greatly saves the cost of the pipeline connection.
Threaded joints refers to the pipeline connecting piece with the screw thread, is a most common pipe in industry. Coupling thread makes connection of the pipe becomes more simple, replacement are also more easily and greatly saves the cost of the pipeline connection.
Threaded joints of industrial is generally made of metal and it can withstand high pressure. The material contents carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, brass, etc.
Hydraulic test
 Hydrostatic test is an inspection method to reduce the risk of flaws in the pipe that might threaten its ability to withstand the maximum operating pressure. Hydrostatic testing inspects the integrity of pipelines by filling in the pipe with a non-compressible liquid (often water, dyed) to increase the pressure level above the normal pressure to see if there is any defect exists. It can either carried out on pipes prior to being put into service or on existing pipes that are already in service.
Hydrostatic test is an inspection method to reduce the risk of flaws in the pipe that might threaten its ability to withstand the maximum operating pressure. Hydrostatic testing inspects the integrity of pipelines by filling in the pipe with a non-compressible liquid (often water, dyed) to increase the pressure level above the normal pressure to see if there is any defect exists. It can either carried out on pipes prior to being put into service or on existing pipes that are already in service.